Cómo Importar Activos 3D Generados por IA en Babylon.js y Three.js

Imagina esto: acabas de crear un impresionante modelo 3D utilizando la tecnología de generador de modelos 3D de IA en segundos, pero ahora te preguntas cómo darle vida en la web. Ya sea que estés construyendo un escaparate de productos interactivo, un juego basado en la web o una experiencia de RA inmersiva, importar tu obra maestra generada por IA en marcos web populares no debería parecer ciencia espacial.
Eso es exactamente lo que resolveremos hoy, con no uno, sino dos enfoques. Comenzaremos con un emocionante atajo impulsado por IA que hará que tu modelo esté en línea en minutos, luego profundizaremos en el método de codificación tradicional para aquellos que desean un control total. Con más de 2 millones de creadores que ya usan Tripo AI para generar modelos 3D profesionales en solo 8-10 segundos, exploremos las formas más rápidas de importar activos 3D generados por IA tanto en Babylon.js como en Three.js.
El Atajo Rápido de IA: Usando Cursor AI para Importar Tu Modelo 3D
Aquí está el cambio de juego: ya no necesitas escribir cientos de líneas de código. Las herramientas de desarrollo impulsadas por IA como Cursor AI pueden generar toda la configuración de integración por ti en minutos, incluso para tareas como la creación de modelos 3D generados por IA. Este método es perfecto para diseñadores, especialistas en marketing y cualquier persona que quiera prototipar rápidamente sin un conocimiento profundo de JavaScript.
¿Por Qué Elegir el Método de Atajo de IA?
- Increíblemente Rápido: Transforma horas de codificación en una configuración de 5 minutos
- Fácil para Principiantes: ¿No tienes experiencia en codificación? No hay problema
- Sin Errores: La IA maneja las partes complejas como la configuración del cargador
- Pruebas Instantáneas: Ve la integración web de tus modelos 3D generados por IA inmediatamente
Paso a Paso: El Método de Cursor AI
1. Exporta Tu Modelo de Tripo AI
Al usar Tripo Studio o la plataforma Tripo AI:
- Genera tu modelo a partir de texto o imagen
- Haz clic en el botón de exportar
- Elige el formato GLB (recomendado para la web)
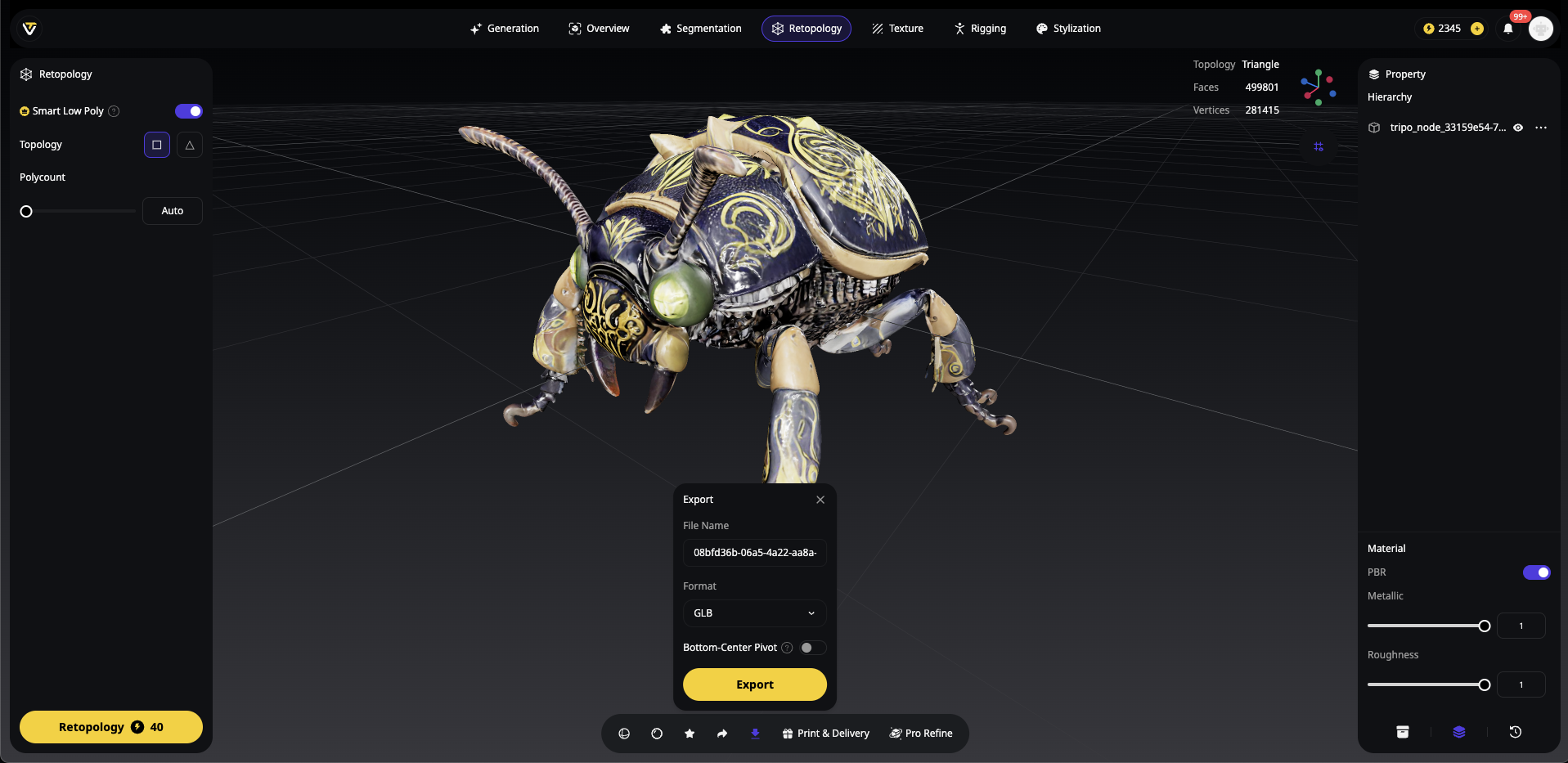
Formatos alternativos: OBJ, FBX, STL o USDZ
Crea una nueva carpeta de proyecto y coloca tu modelo GLB en una subcarpeta models:
my-3d-project/
├── models/
│ └── your-tripo-model.glb
└── (vacío por ahora)
Paso 2: Abre Cursor AI y Crea Tu Prompt
Inicia Cursor AI y abre la carpeta de tu proyecto. Usa este potente prompt para generar todo:
Crea una aplicación web completa que muestre un modelo 3D GLB ubicado en './models/your-tripo-model.glb'.
Requisitos:
1. Configura ejemplos de Babylon.js y Three.js en archivos HTML separados
2. Incluye todas las dependencias necesarias a través de CDN
3. Agrega iluminación adecuada, controles de cámara y un canvas responsivo
4. Implementa controles de órbita para la interacción del usuario
5. Agrega indicadores de progreso de carga
6. Crea un index.html con enlaces a ambos ejemplos
7. Incluye manejo de errores para cargas de modelos fallidas
8. Agrega comentarios explicando cada sección
9. Haz que funcione con 'python -m http.server' para pruebas locales
El modelo debe estar centrado, correctamente iluminado y ser giratorio con controles de ratón.
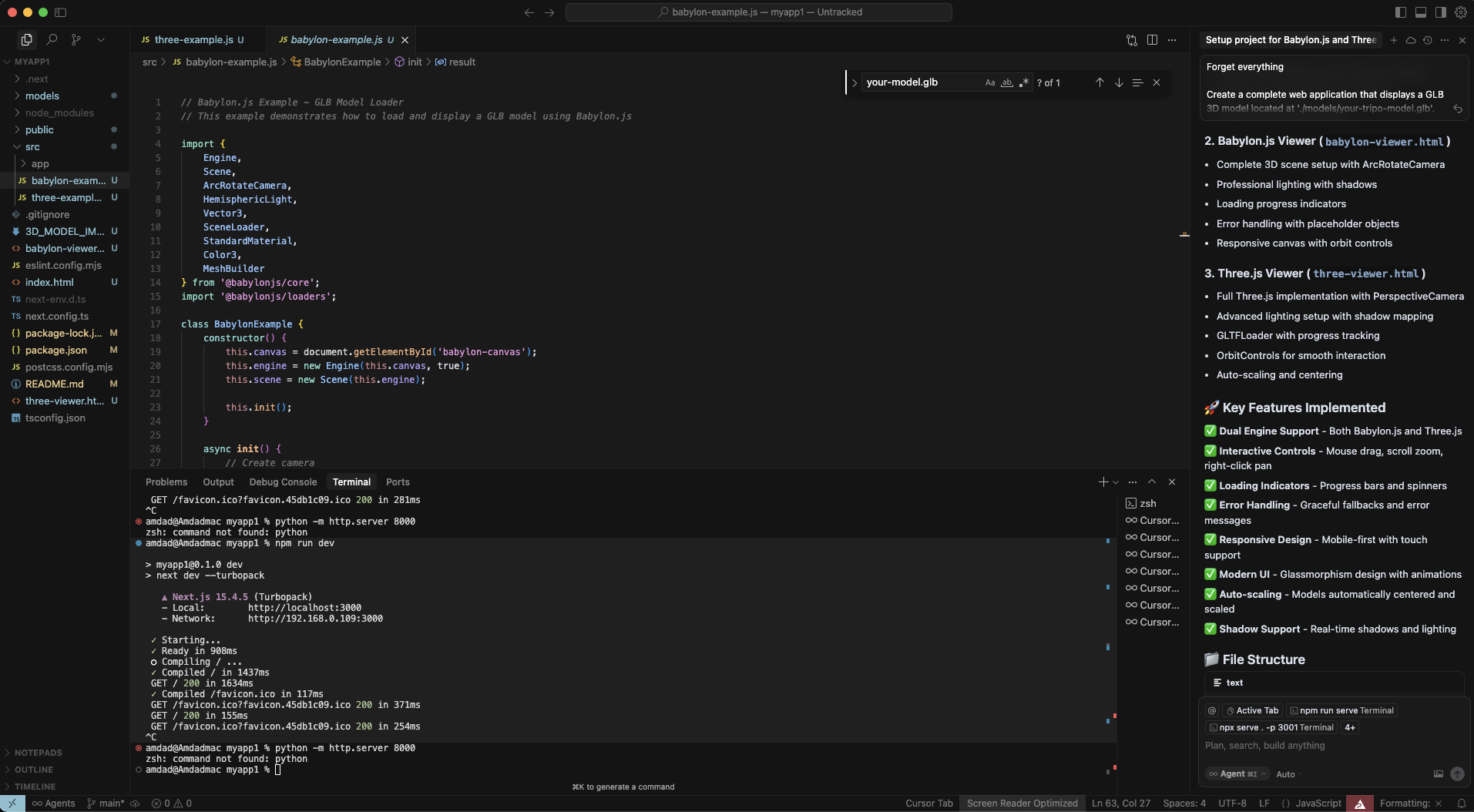
Paso 3: Aplica el Código Generado por IA
Cursor AI generará múltiples archivos. Revisa y acepta los cambios:
index.html - Página de aterrizaje con ambas opciones
babylon-example.html - Implementación de Babylon.js
three-example.html - Implementación de Three.js
Potencialmente un README.md con instrucciones
Paso 4: Prueba Tu Integración
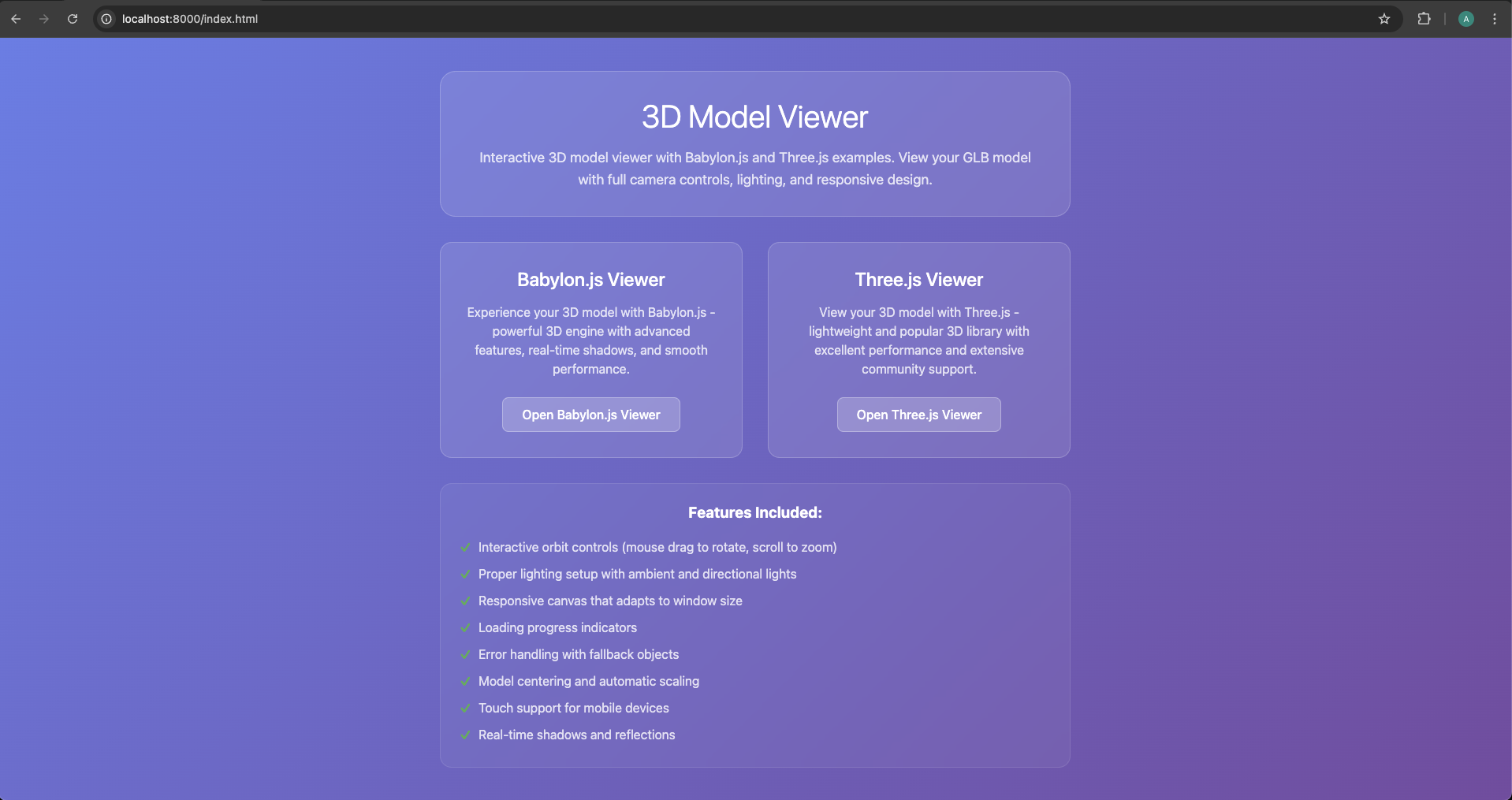
Abre la terminal en la carpeta de tu proyecto y ejecuta:
python -m http.server 8000
# O si prefieres Node.js:
npx http-server
Navega a http://localhost:8000 y haz clic en cualquiera de los ejemplos para ver tu modelo.

Paso 5: Personaliza con Asistencia de IA
¿Necesitas modificaciones? Simplemente pregunta a Cursor AI:
"Agrega un fondo de skybox al ejemplo de Three.js"
"Haz que el modelo rote automáticamente en Babylon.js"
"Agrega efectos de sombra a ambos ejemplos"
"Implementa una pantalla de carga con porcentaje"
Ejemplo Real de Salida de Cursor AI
Esto es lo que Cursor podría generar para tu implementación de Three.js:
_// Ejemplo de Three.js - Cargador de Modelo GLB_
_// Este ejemplo demuestra cómo cargar y mostrar un modelo GLB usando Three.js_
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
class ThreeExample {
constructor() {
this.container = document.getElementById('three-container');
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
this.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
this.renderer.setClearColor(0x000000);
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
this.container.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
this.init();
}
**init**() {
_// Configurar cámara_
this.camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
this.camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
_// Configurar iluminación_
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0x404040, 0.6);
this.scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(10, 10, 5);
directionalLight.castShadow = true;
directionalLight.shadow.mapSize.width = 2048;
directionalLight.shadow.mapSize.height = 2048;
this.scene.add(directionalLight);
_// Agregar OrbitControls_
this.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement);
this.controls.enableDamping = true;
this.controls.dampingFactor = 0.05;
this.controls.screenSpacePanning = false;
this.controls.minDistance = 1;
this.controls.maxDistance = 50;
_// Cargar el modelo GLB_
this.loadModel();
_// Manejar el redimensionamiento de la ventana_
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
this.camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
});
_// Iniciar bucle de animación_
this.animate();
}
**loadModel**() {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
console.log('Cargando modelo GLB...');
loader.load(
'models/your-model1.glb',
(_gltf_) => {
console.log('Modelo cargado exitosamente:', _gltf_);
_// Agregar el modelo a la escena_
this.scene.add(_gltf_.scene);
_// Centrar el modelo_
this.centerModel(_gltf_.scene);
_// Agregar plano de tierra para referencia_
this.createGround();
_// Habilitar sombras para todas las mallas_
_gltf_.scene.traverse((_child_) => {
if (_child_.isMesh) {
_child_.castShadow = true;
_child_.receiveShadow = true;
}
});
},
(_progress_) => {
console.log('Progreso de carga:', (_progress_.loaded / _progress_.total * 100) + '%');
},
(_error_) => {
console.error('Error al cargar el modelo:', _error_);
this.createPlaceholderCube();
}
);
}
**centerModel**(_model_) {
_// Calcular la caja delimitadora para centrar el modelo_
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(_model_);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
_// Centrar el modelo_
_model_.position.sub(center);
_// Escalar el modelo a un tamaño razonable si es necesario_
const maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
if (maxDim > 10) {
const scale = 5 / maxDim;
_model_.scale.setScalar(scale);
}
}
**createGround**() {
_// Crear un plano de tierra para referencia_
const groundGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(20, 20);
const groundMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x333333,
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.8
});
const ground = new THREE.Mesh(groundGeometry, groundMaterial);
ground.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
ground.position.y = -2;
ground.receiveShadow = true;
this.scene.add(ground);
}
**createPlaceholderCube**() {
_// Crear un cubo de marcador de posición si el modelo no se carga_
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(2, 2, 2);
const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({ color: 0x8080ff });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
cube.castShadow = true;
this.scene.add(cube);
}
**animate**() {
requestAnimationFrame(() => this.animate());
_// Actualizar controles_
this.controls.update();
_// Renderizar la escena_
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera);
}
}
_// Inicializar cuando el DOM esté cargado_
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
new ThreeExample();
});
export default ThreeExample;
Comparando Métodos: Atajo de IA vs Codificación Tradicional
El Método Tradicional: Implementación Manual
Si bien los atajos de IA son fantásticos para inicios rápidos, los desarrolladores profesionales a menudo necesitan un control total. Exploremos el enfoque tradicional tanto para la importación de modelos 3D de Babylon.js como para la carga de modelos 3D de Three.js.
Babylon.js: Configuración Manual Completa
Paso 1: Estructura del Proyecto
Crea tu proyecto manualmente:
mkdir babylon-3d-project
cd babylon-3d-project
npm init -y
npm install --save babylonjs babylonjs-loaders
Paso 2: Base HTML
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>Babylon.js - Modelo de Tripo AI</title><style>
html, body {
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#renderCanvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
touch-action: none;
}
</style></head><body><canvas id="renderCanvas"></canvas><script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script><script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/loaders/babylonjs.loaders.min.js"></script><script src="app.js"></script></body></html>
Paso 3: Implementación de JavaScript
// app.jsconst canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true, {
preserveDrawingBuffer: true,
stencil: true,
disableWebGL2Support: false
});
const createScene = async () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
scene.clearColor = new BABYLON.Color4(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 1);
// Cámara con mejor posicionamiento
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera(
"camera",
BABYLON.Tools.ConvertDegreesToRadians(45),
BABYLON.Tools.ConvertDegreesToRadians(60),
10,
BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(),
scene
);
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
camera.wheelPrecision = 50;
camera.minZ = 0.1;
// Configuración de iluminación mejorada
const hemiLight = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight(
"hemiLight",
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0),
scene
);
hemiLight.intensity = 0.5;
const dirLight = new BABYLON.DirectionalLight(
"dirLight",
new BABYLON.Vector3(-1, -2, -1),
scene
);
dirLight.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(20, 40, 20);
dirLight.intensity = 0.5;
dirLight.shadowEnabled = true;
// Generador de sombras
const shadowGenerator = new BABYLON.ShadowGenerator(1024, dirLight);
shadowGenerator.useBlurExponentialShadowMap = true;
// Suelo para sombras
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround(
"ground",
{ width: 20, height: 20 },
scene
);
ground.receiveShadows = true;
// Importar activos 3D generados por IA con manejo de errores
try {
const result = await BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMeshAsync(
"",
"./models/",
"your-tripo-model.glb",
scene
);
// Procesar mallas importadas
result.meshes.forEach(mesh => {
shadowGenerator.addShadowCaster(mesh);
if (mesh.material) {
mesh.material.backFaceCulling = false;
}
});
// Centrar y escalar el modelo
const rootMesh = result.meshes[0];
const bounds = rootMesh.getHierarchyBoundingVectors();
const center = bounds.max.add(bounds.min).scale(0.5);
rootMesh.position = center.negate();
// Ajustar cámara automáticamente
camera.setTarget(BABYLON.Vector3.Zero());
camera.radius = bounds.max.subtract(bounds.min).length() * 1.5;
} catch (error) {
console.error("No se pudo cargar el modelo:", error);
// Crear indicador de error
const errorText = new BABYLON.GUI.TextBlock();
errorText.text = "No se pudo cargar el modelo 3D";
errorText.color = "red";
errorText.fontSize = 24;
}
return scene;
};
// Inicializar y ejecutar
createScene().then(scene => {
engine.runRenderLoop(() => {
scene.render();
});
// Optimización para móviles
engine.setHardwareScalingLevel(1 / window.devicePixelRatio);
});
// Manejo responsivo
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
engine.resize();
});
// Optimización de rendimiento
scene.registerBeforeRender(() => {
// Agrega cualquier actualización por fotograma aquí
});
Three.js: Implementación Profesional
Para cargar modelos 3D en Three.js, aquí está el enfoque manual completo:
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
import { DRACOLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/DRACOLoader.js';
class ThreeJSApp {
constructor() {
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
this.camera = null;
this.renderer = null;
this.controls = null;
this.model = null;
this.mixer = null;
this.clock = new THREE.Clock();
this.init();
this.loadModel();
this.animate();
}
init() {
// Configuración de la escena
this.scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf0f0f0);
this.scene.fog = new THREE.Fog(0xf0f0f0, 10, 50);
// Cámara
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
50,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
this.camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
// Renderer con optimizaciones
this.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,
powerPreference: "high-performance"
});
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2));
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
this.renderer.outputEncoding = THREE.sRGBEncoding;
this.renderer.toneMapping = THREE.ACESFilmicToneMapping;
document.body.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
// Luces
const ambient = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.4);
this.scene.add(ambient);
const directional = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.6);
directional.position.set(5, 10, 5);
directional.castShadow = true;
directional.shadow.camera.near = 0.1;
directional.shadow.camera.far = 50;
directional.shadow.camera.left = -10;
directional.shadow.camera.right = 10;
directional.shadow.camera.top = 10;
directional.shadow.camera.bottom = -10;
directional.shadow.mapSize.width = 2048;
directional.shadow.mapSize.height = 2048;
this.scene.add(directional);
// Suelo
const groundGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(50, 50);
const groundMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0xcccccc,
roughness: 0.8,
metalness: 0.2
});
const ground = new THREE.Mesh(groundGeometry, groundMaterial);
ground.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
ground.receiveShadow = true;
this.scene.add(ground);
// Controles
this.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement);
this.controls.enableDamping = true;
this.controls.dampingFactor = 0.05;
this.controls.screenSpacePanning = false;
this.controls.minDistance = 1;
this.controls.maxDistance = 50;
this.controls.maxPolarAngle = Math.PI / 2;
// Oyentes de eventos
window.addEventListener('resize', this.onWindowResize.bind(this));
}
loadModel() {
// Gestor de carga para el seguimiento del progreso
const manager = new THREE.LoadingManager();
manager.onStart = (url, itemsLoaded, itemsTotal) => {
console.log(`Comenzando la carga: ${url}`);
this.showLoader(true);
};
manager.onProgress = (url, itemsLoaded, itemsTotal) => {
const progress = (itemsLoaded / itemsTotal) * 100;
this.updateLoader(progress);
};
manager.onLoad = () => {
console.log('¡Carga completa!');
this.showLoader(false);
};
manager.onError = (url) => {
console.error(`Error al cargar ${url}`);
this.showError('No se pudo cargar el modelo 3D');
};
// Cargador DRACO para geometría comprimida (opcional pero recomendado)
const dracoLoader = new DRACOLoader(manager);
dracoLoader.setDecoderPath('https://www.gstatic.com/draco/v1/decoders/');
// Cargador GLTF
const loader = new GLTFLoader(manager);
loader.setDRACOLoader(dracoLoader);
// Cargar el modelo
loader.load(
'./models/your-tripo-model.glb',
(gltf) => {
this.model = gltf.scene;
// Centrar y escalar el modelo
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(this.model);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
// Centrar el modelo
this.model.position.sub(center);
// Escalar para ajustar la vista
const maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
const scale = 5 / maxDim;
this.model.scale.multiplyScalar(scale);
// Habilitar sombras
this.model.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
child.castShadow = true;
child.receiveShadow = true;
// Asegurar materiales de doble cara para modelos generados por IA
if (child.material) {
child.material.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
}
}
});
// Agregar a la escena
this.scene.add(this.model);
// Manejar animaciones si están presentes
if (gltf.animations && gltf.animations.length > 0) {
this.mixer = new THREE.AnimationMixer(this.model);
// Reproducir todas las animaciones
gltf.animations.forEach((clip) => {
const action = this.mixer.clipAction(clip);
action.play();
});
}
// Ajustar la cámara para que se ajuste al modelo
this.fitCameraToObject(this.model);
}
);
}
fitCameraToObject(object) {
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(object);
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
const fov = this.camera.fov * (Math.PI / 180);
const cameraZ = Math.abs(maxDim / 2 / Math.tan(fov / 2));
this.camera.position.set(cameraZ, cameraZ, cameraZ);
this.controls.target = center;
this.controls.update();
}
animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate.bind(this));
const delta = this.clock.getDelta();
// Actualizar animaciones
if (this.mixer) {
this.mixer.update(delta);
}
// Actualizar controles
this.controls.update();
// Renderizar
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera);
}
onWindowResize() {
this.camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
}
showLoader(show) {
let loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (!loader && show) {
loader = document.createElement('div');
loader.id = 'loader';
loader.style.cssText = `
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.8);
color: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
z-index: 1000;
`;
document.body.appendChild(loader);
}
if (loader) {
loader.style.display = show ? 'block' : 'none';
}
}
updateLoader(progress) {
const loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (loader) {
loader.textContent = `Cargando: ${Math.round(progress)}%`;
}
}
showError(message) {
const loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (loader) {
loader.textContent = message;
loader.style.background = 'rgba(255,0,0,0.8)';
}
}
}
// Inicializar la aplicación
const app = new ThreeJSApp();
Optimizando Modelos Generados por IA para el Rendimiento Web
Ya sea que hayas usado el atajo de IA o el método manual, optimizar el rendimiento web de tus modelos 3D generados por IA es crucial. Así es como se garantizan experiencias fluidas:
- Optimización del Formato con glTF
El formato de importación de modelos glTF es el estándar de oro para el 3D web. Estas son las razones y cómo optimizar:
// Optimizar texturas durante la carga
loader.load('./models/your-model.glb', (gltf) => {
gltf.scene.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh && child.material) {
// Optimizar texturas
if (child.material.map) {
child.material.map.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipmapLinearFilter;
child.material.map.anisotropy = renderer.capabilities.getMaxAnisotropy();
}
// Habilitar instanciado de GPU para mallas repetidas
if (child.geometry) {
child.geometry.computeBoundingSphere();
child.frustumCulled = true;
}
}
});
});
- Sistema de Nivel de Detalle (LOD)
Implementa LOD para un mejor rendimiento en todos los dispositivos:
class LODManager {
constructor(scene, camera) {
this.scene = scene;
this.camera = camera;
this.lodGroups = new Map();
}
addLODModel(name, levels) {
const lod = new THREE.LOD();
levels.forEach(({ url, distance }) => {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(url, (gltf) => {
lod.addLevel(gltf.scene, distance);
});
});
this.scene.add(lod);
this.lodGroups.set(name, lod);
return lod;
}
update() {
this.lodGroups.forEach(lod => {
lod.update(this.camera);
});
}
}
// Uso
const lodManager = new LODManager(scene, camera);
lodManager.addLODModel('tripoModel', [
{ url: './models/high-detail.glb', distance: 0 },
{ url: './models/medium-detail.glb', distance: 10 },
{ url: './models/low-detail.glb', distance: 20 }
]);
- Compresión de Texturas
Reduce el tamaño de las texturas sin pérdida de calidad:
// Comprimir texturas antes de subirlas a la GPU
function compressTexture(texture) {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Redimensionar a potencia de 2
const size = Math.pow(2, Math.floor(Math.log2(Math.max(texture.image.width, texture.image.height))));
canvas.width = size;
canvas.height = size;
ctx.drawImage(texture.image, 0, 0, size, size);
// Crear textura comprimida
const compressedTexture = new THREE.CanvasTexture(canvas);
compressedTexture.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipmapLinearFilter;
compressedTexture.generateMipmaps = true;
return compressedTexture;
}
- Monitoreo del Rendimiento
Rastrea los FPS y optimiza en consecuencia:
class PerformanceMonitor {
constructor() {
this.fps = 0;
this.frameCount = 0;
this.lastTime = performance.now();
this.createDisplay();
}
createDisplay() {
this.display = document.createElement('div');
this.display.style.cssText = `
position: fixed;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.7);
color: #00ff00;
padding: 10px;
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 14px;
z-index: 1000;
`;
document.body.appendChild(this.display);
}
update() {
this.frameCount++;
const currentTime = performance.now();
if (currentTime >= this.lastTime + 1000) {
this.fps = Math.round((this.frameCount * 1000) / (currentTime - this.lastTime));
this.frameCount = 0;
this.lastTime = currentTime;
this.display.textContent = `FPS: ${this.fps}`;
// Ajustar la calidad automáticamente según los FPS
if (this.fps < 30) {
this.reduceQuality();
} else if (this.fps > 55) {
this.increaseQuality();
}
}
}
reduceQuality() {
// Implementar lógica de reducción de calidad
console.log('Reduciendo calidad para un mejor rendimiento');
}
increaseQuality() {
// Implementar lógica de aumento de calidad
console.log('Aumentando calidad');
}
}
Mejores Prácticas para la Implementación en Producción
- Automatización de la Pipeline de Activos
Crea un proceso de construcción para optimizar automáticamente los modelos 3D para la web:
// package.json
{"scripts": {"optimize-models": "gltf-pipeline -i ./models/raw/*.glb -o ./models/optimized/ -d","build": "npm run optimize-models && webpack"}}
- Implementación de CDN
Sirve tus modelos desde una CDN para un rendimiento global:
const MODEL_CDN = 'https://your-cdn.com/models/';
function loadModelFromCDN(modelName) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(
`${MODEL_CDN}${modelName}`,
resolve,
(progress) => console.log('Cargando:', progress.loaded / progress.total * 100 + '%'),
reject
);
});
}
- Estrategia de Carga Progresiva
Carga modelos según la interacción del usuario:
class ProgressiveLoader {
constructor() {
this.loadQueue = [];
this.isLoading = false;
this.loadedModels = new Map();
}
addToQueue(priority, modelInfo) {
this.loadQueue.push({ priority, ...modelInfo });
this.loadQueue.sort((a, b) => b.priority - a.priority);
this.processQueue();
}
async processQueue() {
if (this.isLoading || this.loadQueue.length === 0) return;
this.isLoading = true;
const { url, name, onLoad } = this.loadQueue.shift();
try {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
const gltf = await loader.loadAsync(url);
this.loadedModels.set(name, gltf.scene);
if (onLoad) onLoad(gltf.scene);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error al cargar ${name}:`, error);
}
this.isLoading = false;
this.processQueue();
}
preloadCritical(models) {
models.forEach(model => {
this.addToQueue(10, model);
});
}
loadOnDemand(modelInfo) {
if (this.loadedModels.has(modelInfo.name)) {
return Promise.resolve(this.loadedModels.get(modelInfo.name));
}
return new Promise((resolve) => {
this.addToQueue(5, {
...modelInfo,
onLoad: resolve
});
});
}
}
// Ejemplo de uso
const loader = new ProgressiveLoader();
// Precargar modelos críticos
loader.preloadCritical([
{ name: 'hero-model', url: './models/hero.glb' },
{ name: 'environment', url: './models/environment.glb' }
]);
// Cargar bajo demanda por interacción del usuario
document.getElementById('load-extra').addEventListener('click', async () => {
const model = await loader.loadOnDemand({
name: 'extra-model',
url: './models/extra.glb'
});
scene.add(model);
});
- Gestión de Memoria
Libera correctamente los activos no utilizados para evitar fugas de memoria:
class ResourceManager {
constructor() {
this.resources = new Map();
}
addResource(name, resource) {
this.resources.set(name, resource);
}
disposeResource(name) {
const resource = this.resources.get(name);
if (!resource) return;
resource.traverse((child) => {
if (child.geometry) {
child.geometry.dispose();
}
if (child.material) {
if (Array.isArray(child.material)) {
child.material.forEach(mat => this.disposeMaterial(mat));
} else {
this.disposeMaterial(child.material);
}
}
});
this.resources.delete(name);
}
disposeMaterial(material) {
// Liberar texturas
['map', 'normalMap', 'roughnessMap', 'metalnessMap', 'aoMap'].forEach(prop => {
if (material[prop]) {
material[prop].dispose();
}
});
material.dispose();
}
disposeAll() {
this.resources.forEach((resource, name) => {
this.disposeResource(name);
});
}
}
Errores Comunes y Soluciones
Guía de Solución de Problemas
Optimizaciones Específicas del Dispositivo
class DeviceOptimizer {
constructor(renderer) {
this.renderer = renderer;
this.isMobile = /Android|webOS|iPhone|iPad|iPod/i.test(navigator.userAgent);
this.gpu = this.detectGPU();
this.applyOptimizations();
}
detectGPU() {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
const debugInfo = gl.getExtension('WEBGL_debug_renderer_info');
if (debugInfo) {
return gl.getParameter(debugInfo.UNMASKED_RENDERER_WEBGL);
}
return 'unknown';
}
applyOptimizations() {
if (this.isMobile) {
// Optimizaciones para móvil
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2));
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = false;
// Reducir tamaño de texturas
THREE.DefaultLoadingManager.onLoad = () => {
this.renderer.capabilities.maxTextureSize = 2048;
};
} else {
// Optimizaciones para escritorio
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
}
// Configuraciones específicas de GPU
if (this.gpu.includes('Intel')) {
console.log('GPU Intel detectada, aplicando configuraciones conservadoras');
this.renderer.capabilities.precision = 'mediump';
}
}
getRecommendedModelQuality() {
if (this.isMobile) return 'low';
if (this.gpu.includes('Intel')) return 'medium';
return 'high';
}
}
// Uso
const optimizer = new DeviceOptimizer(renderer);
const quality = optimizer.getRecommendedModelQuality();
Integración con Marcos Modernos
Ejemplo de Integración con React
// TripoModelViewer.jsx
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls';
const TripoModelViewer = ({ modelUrl, width = '100%', height = '500px' }) => {
const mountRef = useRef(null);
const sceneRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const mount = mountRef.current;
// Configuración de la escena
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf0f0f0);
// Cámara
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
50,
mount.clientWidth / mount.clientHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
// Renderer
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize(mount.clientWidth, mount.clientHeight);
mount.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// Luces
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.6);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(5, 10, 5);
scene.add(directionalLight);
// Controles
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.enableDamping = true;
// Cargar modelo
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(modelUrl, (gltf) => {
scene.add(gltf.scene);
// Centrado y escalado automático
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(gltf.scene);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
gltf.scene.position.sub(center);
});
// Bucle de animación
const animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
animate();
// Manejar redimensionamiento
const handleResize = () => {
camera.aspect = mount.clientWidth / mount.clientHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(mount.clientWidth, mount.clientHeight);
};
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
// Almacenar referencia de la escena
sceneRef.current = { scene, camera, renderer, controls };
// Limpieza
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
mount.removeChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.dispose();
};
}, [modelUrl]);
return <div ref={mountRef} />;
};
export default TripoModelViewer;
// Uso en tu aplicación React
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Mi Modelo de Tripo AI</h1>
<TripoModelViewer modelUrl="./models/my-model.glb" />
</div>
);
}
Integración con Vue.js
// TripoModelViewer.vue
<template>
<div ref="container" :style="{ width: width, height: height }"></div>
</template>
<script>
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls';
export default {
name: 'TripoModelViewer',
props: {
modelUrl: String,
width: { type: String, default: '100%' },
height: { type: String, default: '500px' }
},
mounted() {
this.initThree();
this.loadModel();
},
methods: {
initThree() {
// Configuración de Three.js similar al ejemplo de React
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
// ... resto de la inicialización
},
loadModel() {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(this.modelUrl, (gltf) => {
this.scene.add(gltf.scene);
});
}
},
beforeDestroy() {
// Limpieza de recursos de Three.js
if (this.renderer) {
this.renderer.dispose();
}
}
};
</script>
Benchmarking de Rendimiento
Rastrea y optimiza el rendimiento web de tus modelos 3D generados por IA:
class PerformanceBenchmark {
constructor() {
this.metrics = {
loadTime: 0,
frameRate: [],
memoryUsage: [],
drawCalls: 0
};
}
startLoadTimer() {
this.loadStart = performance.now();
}
endLoadTimer() {
this.metrics.loadTime = performance.now() - this.loadStart;
console.log(`Modelo cargado en ${this.metrics.loadTime.toFixed(2)}ms`);
}
measureFrame(renderer) {
// Velocidad de fotogramas
this.metrics.frameRate.push(renderer.info.render.frame);
// Uso de memoria
if (performance.memory) {
this.metrics.memoryUsage.push({
used: performance.memory.usedJSHeapSize / 1048576,
total: performance.memory.totalJSHeapSize / 1048576
});
}
// Llamadas de dibujo
this.metrics.drawCalls = renderer.info.render.calls;
}
getReport() {
const avgFrameRate = this.metrics.frameRate.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / this.metrics.frameRate.length;
const avgMemory = this.metrics.memoryUsage.reduce((a, b) => a + b.used, 0) / this.metrics.memoryUsage.length;
return {
loadTime: `${this.metrics.loadTime.toFixed(2)}ms`,
avgFrameRate: avgFrameRate.toFixed(2),
avgMemoryMB: avgMemory.toFixed(2),
drawCalls: this.metrics.drawCalls
};
}
}
Conclusión: El Futuro del Desarrollo Web 3D
Hemos cubierto dos potentes enfoques para importar activos 3D generados por IA en marcos web. El atajo asistido por IA con Cursor AI democratiza el desarrollo web 3D, haciéndolo accesible a creadores sin un conocimiento profundo de codificación. Mientras tanto, el enfoque manual tradicional proporciona el control preciso que los desarrolladores profesionales necesitan para aplicaciones complejas.
La combinación de las capacidades de generación instantánea de modelos 3D por IA de Tripo AI y los marcos web modernos crea oportunidades sin precedentes:
-
Prototipos Rápidos: De la idea al 3D interactivo en minutos, no en semanas
-
Eficiencia de Costos: No se necesitan costosos artistas 3D para cada proyecto
-
Escalabilidad: Genera e implementa miles de modelos únicos
-
Accesibilidad: Cualquiera puede crear experiencias web 3D profesionales
Ya sea que estés construyendo un sitio de comercio electrónico con vistas de productos en 3D, un juego basado en la web o una plataforma educativa, el flujo de trabajo desde Tripo AI hasta la implementación web nunca ha sido tan fluido. Con el Algoritmo 2.5 generando modelos impresionantes en solo 8-10 segundos, y los métodos de importación que hemos cubierto, estás equipado para crear experiencias que habrían sido imposibles hace solo unos años.
¿Listo para transformar tus proyectos web con contenido 3D impulsado por IA? Únete a más de 2 millones de creadores que ya usan Tripo AI. Genera tu primer modelo gratis y velo cobrar vida en tu navegador en minutos. El futuro del 3D web no se trata de flujos de trabajo complejos, se trata de dar vida a las ideas al instante.
¡Empieza a crear hoy mismo y descubre por qué Tripo AI es la opción preferida para desarrolladores y diseñadores de todo el mundo! Tu próxima experiencia 3D web innovadora está a solo unos clics de distancia.
Advancing 3D generation to new heights
moving at the speed of creativity, achieving the depths of imagination.

