How to Import AI-Generated 3D Assets into Babylon.js and Three.js

Picture this: You've just created a stunning 3D model using AI 3D model generator technology in seconds, but now you're stuck wondering how to bring it to life on the web. Whether you're building an interactive product showcase, a web-based game, or an immersive AR experience, importing your AI-generated masterpiece into popular web frameworks shouldn't feel like rocket science.
That's exactly what we'll solve today—with not one, but two approaches. We'll start with an exciting AI-powered shortcut that gets your model live in minutes, then dive into the traditional coding method for those who want full control. With over 2 million creators already using Tripo AI to generate professional 3D models in just 8-10 seconds, let's explore the fastest ways to import AI generated 3D assets into both Babylon.js and Three.js.
The Quick AI Shortcut: Using Cursor AI to Import Your 3D Model
Here's the game-changer: You don't need to write hundreds of lines of code anymore. AI-powered development tools like Cursor AI can generate the entire integration setup for you in minutes, including for tasks like creating ai generated 3d models. This method is perfect for designers, marketers, and anyone who wants to prototype quickly without deep JavaScript knowledge.
Why Choose the AI Shortcut Method?
- Lightning Fast: Transform hours of coding into a 5-minute setup
- Beginner-Friendly: No coding experience? No problem
- Error-Free: AI handles the complex parts like loader configuration
- Instant Testing: See your AI generated 3D models web integration immediately
Step-by-Step: The Cursor AI Method
1. Export Your Tripo AI Model
When using Tripo Studio or the Tripo AI platform:
- Generate your model from text or image
- Click the export button
- Choose GLB format (recommended for web)
Alternative formats: OBJ, FBX, STL, or USDZ
Create a new project folder and place your GLB model in a models subfolder:
my-3d-project/
├── models/
│ └── your-tripo-model.glb
└── (empty for now)
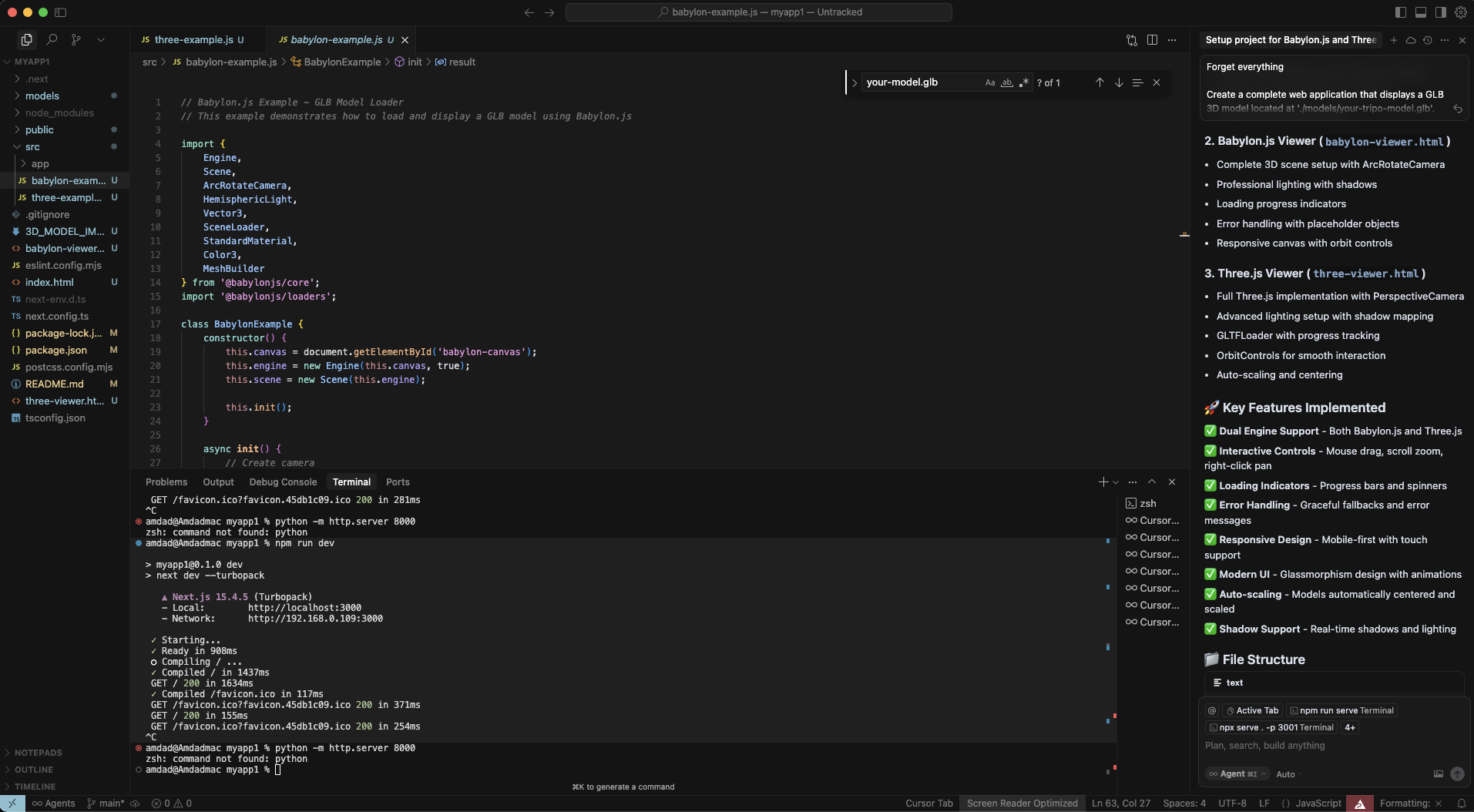
Step 2: Open Cursor AI and Create Your Prompt
Launch Cursor AI and open your project folder. Use this powerful prompt to generate everything:
Create a complete web application that displays a GLB 3D model located at './models/your-tripo-model.glb'.
Requirements:
1. Set up both Babylon.js and Three.js examples in separate HTML files
2. Include all necessary dependencies via CDN
3. Add proper lighting, camera controls, and responsive canvas
4. Implement orbit controls for user interaction
5. Add loading progress indicators
6. Create an index.html with links to both examples
7. Include error handling for failed model loads
8. Add comments explaining each section
9. Make it work with 'python -m http.server' for local testing
The model should be centered, properly lit, and rotatable with mouse controls.
Step 3: Apply AI-Generated Code
Cursor AI will generate multiple files. Review and accept the changes:
index.html - Landing page with both options
babylon-example.html - Babylon.js implementation
three-example.html - Three.js implementation
Potentially a README.md with instructions
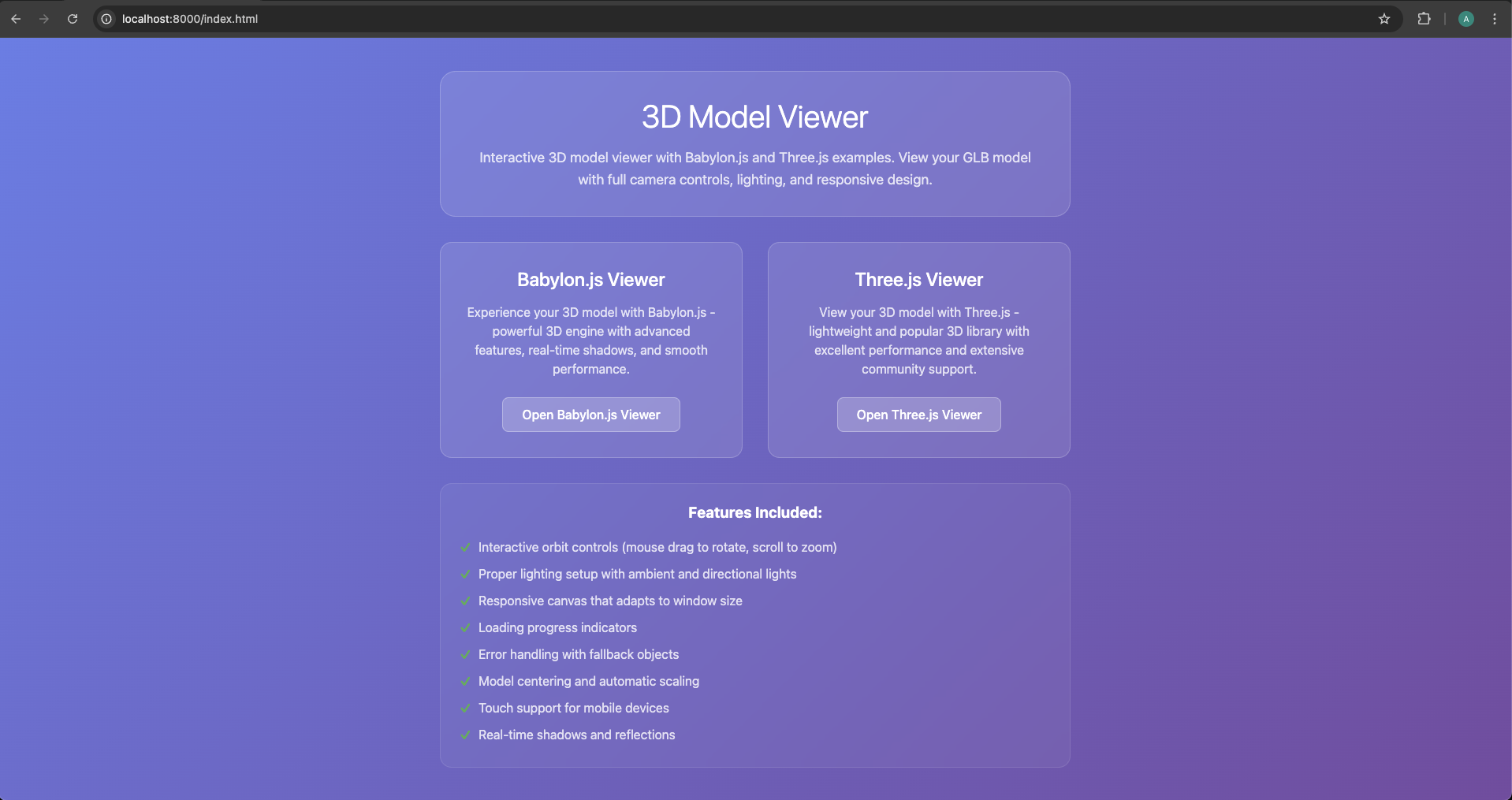
Step 4: Test Your Integration
Open terminal in your project folder and run:
python -m http.server 8000
# Or if you prefer Node.js:
npx http-server
Navigate to http://localhost:8000 and click either example to see your model!

Step 5: Customize with AI Assistance
Need modifications? Simply ask Cursor AI:
"Add a skybox background to the Three.js example"
"Make the model rotate automatically in Babylon.js"
"Add shadow effects to both examples"
"Implement a loading screen with percentage"
Real Example Output from Cursor AI
Here's what Cursor might generate for your Three.js implementation:
_// Three.js Example - GLB Model Loader_
_// This example demonstrates how to load and display a GLB model using Three.js_
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
class ThreeExample {
constructor() {
this.container = document.getElementById('three-container');
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
this.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
this.renderer.setClearColor(0x000000);
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
this.container.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
this.init();
}
**init**() {
_// Set up camera_
this.camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
this.camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
_// Set up lighting_
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0x404040, 0.6);
this.scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(10, 10, 5);
directionalLight.castShadow = true;
directionalLight.shadow.mapSize.width = 2048;
directionalLight.shadow.mapSize.height = 2048;
this.scene.add(directionalLight);
_// Add OrbitControls_
this.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement);
this.controls.enableDamping = true;
this.controls.dampingFactor = 0.05;
this.controls.screenSpacePanning = false;
this.controls.minDistance = 1;
this.controls.maxDistance = 50;
_// Load the GLB model_
this.loadModel();
_// Handle window resize_
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
this.camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
});
_// Start animation loop_
this.animate();
}
**loadModel**() {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
console.log('Loading GLB model...');
loader.load(
'models/your-model1.glb',
(_gltf_) => {
console.log('Model loaded successfully:', _gltf_);
_// Add the model to the scene_
this.scene.add(_gltf_.scene);
_// Center the model_
this.centerModel(_gltf_.scene);
_// Add ground plane for reference_
this.createGround();
_// Enable shadows for all meshes_
_gltf_.scene.traverse((_child_) => {
if (_child_.isMesh) {
_child_.castShadow = true;
_child_.receiveShadow = true;
}
});
},
(_progress_) => {
console.log('Loading progress:', (_progress_.loaded / _progress_.total * 100) + '%');
},
(_error_) => {
console.error('Error loading model:', _error_);
this.createPlaceholderCube();
}
);
}
**centerModel**(_model_) {
_// Calculate bounding box to center the model_
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(_model_);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
_// Center the model_
_model_.position.sub(center);
_// Scale model to reasonable size if needed_
const maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
if (maxDim > 10) {
const scale = 5 / maxDim;
_model_.scale.setScalar(scale);
}
}
**createGround**() {
_// Create a ground plane for reference_
const groundGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(20, 20);
const groundMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x333333,
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.8
});
const ground = new THREE.Mesh(groundGeometry, groundMaterial);
ground.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
ground.position.y = -2;
ground.receiveShadow = true;
this.scene.add(ground);
}
**createPlaceholderCube**() {
_// Create a placeholder cube if model fails to load_
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(2, 2, 2);
const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({ color: 0x8080ff });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
cube.castShadow = true;
this.scene.add(cube);
}
**animate**() {
requestAnimationFrame(() => this.animate());
_// Update controls_
this.controls.update();
_// Render the scene_
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera);
}
}
_// Initialize when DOM is loaded_
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
new ThreeExample();
});
export default ThreeExample;
Comparing Methods: AI Shortcut vs Traditional Coding
The Traditional Method: Manual Implementation
While AI shortcuts are fantastic for quick starts, professional developers often need full control. Let's explore the traditional approach for both Babylon.js 3D model import and Three.js load 3D models.
Babylon.js: Complete Manual Setup
Step 1: Project Structure
Create your project manually:
mkdir babylon-3d-project
cd babylon-3d-project
npm init -y
npm install --save babylonjs babylonjs-loaders
Step 2: HTML Foundation
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>Babylon.js - Tripo AI Model</title><style>
html, body {
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#renderCanvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
touch-action: none;
}
</style></head><body><canvas id="renderCanvas"></canvas><script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script><script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/loaders/babylonjs.loaders.min.js"></script><script src="app.js"></script></body></html>
Step 3: JavaScript Implementation
// app.jsconst canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true, {
preserveDrawingBuffer: true,
stencil: true,
disableWebGL2Support: false
});
const createScene = async () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
scene.clearColor = new BABYLON.Color4(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 1);
// Camera with better positioningconst camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera(
"camera",
BABYLON.Tools.ConvertDegreesToRadians(45),
BABYLON.Tools.ConvertDegreesToRadians(60),
10,
BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(),
scene
);
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
camera.wheelPrecision = 50;
camera.minZ = 0.1;
// Enhanced lighting setupconst hemiLight = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight(
"hemiLight",
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0),
scene
);
hemiLight.intensity = 0.5;
const dirLight = new BABYLON.DirectionalLight(
"dirLight",
new BABYLON.Vector3(-1, -2, -1),
scene
);
dirLight.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(20, 40, 20);
dirLight.intensity = 0.5;
dirLight.shadowEnabled = true;
// Shadow generatorconst shadowGenerator = new BABYLON.ShadowGenerator(1024, dirLight);
shadowGenerator.useBlurExponentialShadowMap = true;
// Ground for shadowsconst ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround(
"ground",
{ width: 20, height: 20 },
scene
);
ground.receiveShadows = true;
// Import AI generated 3D assets with error handlingtry {
const result = await BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMeshAsync(
"",
"./models/",
"your-tripo-model.glb",
scene
);
// Process imported meshes
result.meshes.forEach(mesh => {
shadowGenerator.addShadowCaster(mesh);
if (mesh.material) {
mesh.material.backFaceCulling = false;
}
});
// Center and scale modelconst rootMesh = result.meshes[0];
const bounds = rootMesh.getHierarchyBoundingVectors();
const center = bounds.max.add(bounds.min).scale(0.5);
rootMesh.position = center.negate();
// Auto-fit camera
camera.setTarget(BABYLON.Vector3.Zero());
camera.radius = bounds.max.subtract(bounds.min).length() * 1.5;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to load model:", error);
// Create error indicatorconst errorText = new BABYLON.GUI.TextBlock();
errorText.text = "Failed to load 3D model";
errorText.color = "red";
errorText.fontSize = 24;
}
return scene;
};
// Initialize and runcreateScene().then(scene => {
engine.runRenderLoop(() => {
scene.render();
});
// Optimization for mobile
engine.setHardwareScalingLevel(1 / window.devicePixelRatio);
});
// Responsive handlingwindow.addEventListener("resize", () => {
engine.resize();
});
// Performance optimization
scene.registerBeforeRender(() => {
// Add any per-frame updates here
});
Three.js: Professional Implementation
For Three.js load 3D models, here's the complete manual approach:
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js';
import { DRACOLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/DRACOLoader.js';
class ThreeJSApp {
constructor() {
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
this.camera = null;
this.renderer = null;
this.controls = null;
this.model = null;
this.mixer = null;
this.clock = new THREE.Clock();
this.init();
this.loadModel();
this.animate();
}
init() {
// Scene setupthis.scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf0f0f0);
this.scene.fog = new THREE.Fog(0xf0f0f0, 10, 50);
// Camerathis.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
50,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
this.camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
// Renderer with optimizationsthis.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,
powerPreference: "high-performance"
});
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2));
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
this.renderer.outputEncoding = THREE.sRGBEncoding;
this.renderer.toneMapping = THREE.ACESFilmicToneMapping;
document.body.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
// Lightsconst ambient = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.4);
this.scene.add(ambient);
const directional = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.6);
directional.position.set(5, 10, 5);
directional.castShadow = true;
directional.shadow.camera.near = 0.1;
directional.shadow.camera.far = 50;
directional.shadow.camera.left = -10;
directional.shadow.camera.right = 10;
directional.shadow.camera.top = 10;
directional.shadow.camera.bottom = -10;
directional.shadow.mapSize.width = 2048;
directional.shadow.mapSize.height = 2048;
this.scene.add(directional);
// Groundconst groundGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(50, 50);
const groundMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0xcccccc,
roughness: 0.8,
metalness: 0.2
});
const ground = new THREE.Mesh(groundGeometry, groundMaterial);
ground.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
ground.receiveShadow = true;
this.scene.add(ground);
// Controlsthis.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement);
this.controls.enableDamping = true;
this.controls.dampingFactor = 0.05;
this.controls.screenSpacePanning = false;
this.controls.minDistance = 1;
this.controls.maxDistance = 50;
this.controls.maxPolarAngle = Math.PI / 2;
// Event listenerswindow.addEventListener('resize', this.onWindowResize.bind(this));
}
loadModel() {
// Loading manager for progress trackingconst manager = new THREE.LoadingManager();
manager.onStart = (url, itemsLoaded, itemsTotal) => {
console.log(`Started loading: ${url}`);
this.showLoader(true);
};
manager.onProgress = (url, itemsLoaded, itemsTotal) => {
const progress = (itemsLoaded / itemsTotal) * 100;
this.updateLoader(progress);
};
manager.onLoad = () => {
console.log('Loading complete!');
this.showLoader(false);
};
manager.onError = (url) => {
console.error(`Error loading ${url}`);
this.showError('Failed to load 3D model');
};
// DRACO loader for compressed geometry (optional but recommended)const dracoLoader = new DRACOLoader(manager);
dracoLoader.setDecoderPath('https://www.gstatic.com/draco/v1/decoders/');
// GLTF loaderconst loader = new GLTFLoader(manager);
loader.setDRACOLoader(dracoLoader);
// Load the model
loader.load(
'./models/your-tripo-model.glb',
(gltf) => {
this.model = gltf.scene;
// Center and scale the modelconst box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(this.model);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
// Center the modelthis.model.position.sub(center);
// Scale to fit viewconst maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
const scale = 5 / maxDim;
this.model.scale.multiplyScalar(scale);
// Enable shadowsthis.model.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
child.castShadow = true;
child.receiveShadow = true;
// Ensure double-sided materials for AI-generated modelsif (child.material) {
child.material.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
}
}
});
// Add to scenethis.scene.add(this.model);
// Handle animations if presentif (gltf.animations && gltf.animations.length > 0) {
this.mixer = new THREE.AnimationMixer(this.model);
// Play all animations
gltf.animations.forEach((clip) => {
const action = this.mixer.clipAction(clip);
action.play();
});
}
// Adjust camera to fit modelthis.fitCameraToObject(this.model);
}
);
}
fitCameraToObject(object) {
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(object);
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const maxDim = Math.max(size.x, size.y, size.z);
const fov = this.camera.fov * (Math.PI / 180);
const cameraZ = Math.abs(maxDim / 2 / Math.tan(fov / 2));
this.camera.position.set(cameraZ, cameraZ, cameraZ);
this.controls.target = center;
this.controls.update();
}
animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate.bind(this));
const delta = this.clock.getDelta();
// Update animationsif (this.mixer) {
this.mixer.update(delta);
}
// Update controlsthis.controls.update();
// Renderthis.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera);
}
onWindowResize() {
this.camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
this.renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
}
showLoader(show) {
let loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (!loader && show) {
loader = document.createElement('div');
loader.id = 'loader';
loader.style.cssText = `
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.8);
color: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
z-index: 1000;
`;
document.body.appendChild(loader);
}
if (loader) {
loader.style.display = show ? 'block' : 'none';
}
}
updateLoader(progress) {
const loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (loader) {
loader.textContent = `Loading: ${Math.round(progress)}%`;
}
}
showError(message) {
const loader = document.getElementById('loader');
if (loader) {
loader.textContent = message;
loader.style.background = 'rgba(255,0,0,0.8)';
}
}
}
// Initialize the appconst app = new ThreeJSApp();
Optimizing AI-Generated Models for Web Performance
Whether you used the AI shortcut or manual method, optimizing your AI generated 3D models web performance is crucial. Here's how to ensure smooth experiences:
- Format Optimization with glTF
The glTF model import format is the gold standard for web 3D. Here's why and how to optimize:
// Optimize textures during loading
loader.load('./models/your-model.glb', (gltf) => {
gltf.scene.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh && child.material) {
// Optimize texturesif (child.material.map) {
child.material.map.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipmapLinearFilter;
child.material.map.anisotropy = renderer.capabilities.getMaxAnisotropy();
}
// Enable GPU instancing for repeated meshesif (child.geometry) {
child.geometry.computeBoundingSphere();
child.frustumCulled = true;
}
}
});
});
- Level of Detail (LOD) System
Implement LOD for better performance across devices:
class LODManager {
constructor(scene, camera) {
this.scene = scene;
this.camera = camera;
this.lodGroups = new Map();
}
addLODModel(name, levels) {
const lod = new THREE.LOD();
levels.forEach(({ url, distance }) => {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(url, (gltf) => {
lod.addLevel(gltf.scene, distance);
});
});
this.scene.add(lod);
this.lodGroups.set(name, lod);
return lod;
}
update() {
this.lodGroups.forEach(lod => {
lod.update(this.camera);
});
}
}
// Usageconst lodManager = new LODManager(scene, camera);
lodManager.addLODModel('tripoModel', [
{ url: './models/high-detail.glb', distance: 0 },
{ url: './models/medium-detail.glb', distance: 10 },
{ url: './models/low-detail.glb', distance: 20 }
]);
- Texture Compression
Reduce texture sizes without quality loss:
// Compress textures before upload to GPUfunction compressTexture(texture) {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Resize to power of 2const size = Math.pow(2, Math.floor(Math.log2(Math.max(texture.image.width, texture.image.height))));
canvas.width = size;
canvas.height = size;
ctx.drawImage(texture.image, 0, 0, size, size);
// Create compressed textureconst compressedTexture = new THREE.CanvasTexture(canvas);
compressedTexture.minFilter = THREE.LinearMipmapLinearFilter;
compressedTexture.generateMipmaps = true;
return compressedTexture;
}
- Performance Monitoring
Track FPS and optimize accordingly:
class PerformanceMonitor {
constructor() {
this.fps = 0;
this.frameCount = 0;
this.lastTime = performance.now();
this.createDisplay();
}
createDisplay() {
this.display = document.createElement('div');
this.display.style.cssText = `
position: fixed;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.7);
color: #00ff00;
padding: 10px;
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 14px;
z-index: 1000;
`;
document.body.appendChild(this.display);
}
update() {
this.frameCount++;
const currentTime = performance.now();
if (currentTime >= this.lastTime + 1000) {
this.fps = Math.round((this.frameCount * 1000) / (currentTime - this.lastTime));
this.frameCount = 0;
this.lastTime = currentTime;
this.display.textContent = `FPS: ${this.fps}`;
// Auto-adjust quality based on FPSif (this.fps < 30) {
this.reduceQuality();
} else if (this.fps > 55) {
this.increaseQuality();
}
}
}
reduceQuality() {
// Implement quality reduction logicconsole.log('Reducing quality for better performance');
}
increaseQuality() {
// Implement quality increase logicconsole.log('Increasing quality');
}
}
Best Practices for Production Deployment
- Asset Pipeline Automation
Create a build process to optimize 3D models for web automatically:
// package.json{"scripts": {"optimize-models": "gltf-pipeline -i ./models/raw/*.glb -o ./models/optimized/ -d","build": "npm run optimize-models && webpack"}}
- CDN Deployment
Serve your models from a CDN for global performance:
const MODEL_CDN = 'https://your-cdn.com/models/';
function loadModelFromCDN(modelName) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(
`${MODEL_CDN}${modelName}`,
resolve,
(progress) => console.log('Loading:', progress.loaded / progress.total * 100 + '%'),
reject
);
});
}
- Progressive Loading Strategy
Load models based on user interaction:
class ProgressiveLoader {
constructor() {
this.loadQueue = [];
this.isLoading = false;
this.loadedModels = new Map();
}
addToQueue(priority, modelInfo) {
this.loadQueue.push({ priority, ...modelInfo });
this.loadQueue.sort((a, b) => b.priority - a.priority);
this.processQueue();
}
async processQueue() {
if (this.isLoading || this.loadQueue.length === 0) return;
this.isLoading = true;
const { url, name, onLoad } = this.loadQueue.shift();
try {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
const gltf = await loader.loadAsync(url);
this.loadedModels.set(name, gltf.scene);
if (onLoad) onLoad(gltf.scene);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Failed to load ${name}:`, error);
}
this.isLoading = false;
this.processQueue();
}
preloadCritical(models) {
models.forEach(model => {
this.addToQueue(10, model);
});
}
loadOnDemand(modelInfo) {
if (this.loadedModels.has(modelInfo.name)) {
return Promise.resolve(this.loadedModels.get(modelInfo.name));
}
return new Promise((resolve) => {
this.addToQueue(5, {
...modelInfo,
onLoad: resolve
});
});
}
}
// Usage exampleconst loader = new ProgressiveLoader();
// Preload critical models
loader.preloadCritical([
{ name: 'hero-model', url: './models/hero.glb' },
{ name: 'environment', url: './models/environment.glb' }
]);
// Load on user interactiondocument.getElementById('load-extra').addEventListener('click', async () => {
const model = await loader.loadOnDemand({
name: 'extra-model',
url: './models/extra.glb'
});
scene.add(model);
});
- Memory Management
Properly dispose of unused assets to prevent memory leaks:
class ResourceManager {
constructor() {
this.resources = new Map();
}
addResource(name, resource) {
this.resources.set(name, resource);
}
disposeResource(name) {
const resource = this.resources.get(name);
if (!resource) return;
resource.traverse((child) => {
if (child.geometry) {
child.geometry.dispose();
}
if (child.material) {
if (Array.isArray(child.material)) {
child.material.forEach(mat => this.disposeMaterial(mat));
} else {
this.disposeMaterial(child.material);
}
}
});
this.resources.delete(name);
}
disposeMaterial(material) {
// Dispose textures
['map', 'normalMap', 'roughnessMap', 'metalnessMap', 'aoMap'].forEach(prop => {
if (material[prop]) {
material[prop].dispose();
}
});
material.dispose();
}
disposeAll() {
this.resources.forEach((resource, name) => {
this.disposeResource(name);
});
}
}
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Troubleshooting Guide
Device-Specific Optimizations
class DeviceOptimizer {
constructor(renderer) {
this.renderer = renderer;
this.isMobile = /Android|webOS|iPhone|iPad|iPod/i.test(navigator.userAgent);
this.gpu = this.detectGPU();
this.applyOptimizations();
}
detectGPU() {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
const debugInfo = gl.getExtension('WEBGL_debug_renderer_info');
if (debugInfo) {
return gl.getParameter(debugInfo.UNMASKED_RENDERER_WEBGL);
}
return 'unknown';
}
applyOptimizations() {
if (this.isMobile) {
// Mobile optimizationsthis.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2));
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = false;
// Reduce texture sizesTHREE.DefaultLoadingManager.onLoad = () => {
this.renderer.capabilities.maxTextureSize = 2048;
};
} else {
// Desktop optimizationsthis.renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap;
}
// GPU-specific settingsif (this.gpu.includes('Intel')) {
console.log('Intel GPU detected, applying conservative settings');
this.renderer.capabilities.precision = 'mediump';
}
}
getRecommendedModelQuality() {
if (this.isMobile) return 'low';
if (this.gpu.includes('Intel')) return 'medium';
return 'high';
}
}
// Usageconst optimizer = new DeviceOptimizer(renderer);
const quality = optimizer.getRecommendedModelQuality();
Integration with Modern Frameworks
React Integration Example
// TripoModelViewer.jsximport React, { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls';
const TripoModelViewer = ({ modelUrl, width = '100%', height = '500px' }) => {
const mountRef = useRef(null);
const sceneRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const mount = mountRef.current;
// Scene setupconst scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xf0f0f0);
// Cameraconst camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
50,
mount.clientWidth / mount.clientHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
camera.position.set(5, 5, 5);
// Rendererconst renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize(mount.clientWidth, mount.clientHeight);
mount.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// Lightsconst ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.6);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(5, 10, 5);
scene.add(directionalLight);
// Controlsconst controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.enableDamping = true;
// Load modelconst loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(modelUrl, (gltf) => {
scene.add(gltf.scene);
// Auto-center and scaleconst box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(gltf.scene);
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
gltf.scene.position.sub(center);
});
// Animation loopconst animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
animate();
// Handle resizeconst handleResize = () => {
camera.aspect = mount.clientWidth / mount.clientHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(mount.clientWidth, mount.clientHeight);
};
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
// Store scene reference
sceneRef.current = { scene, camera, renderer, controls };
// Cleanupreturn () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
mount.removeChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.dispose();
};
}, [modelUrl]);
return <div ref={mountRef} />;
};
export default TripoModelViewer;
// Usage in your React appfunction App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My Tripo AI Model</h1>
<TripoModelViewer modelUrl="./models/my-model.glb" />
</div>
);
}
Vue.js Integration
// TripoModelViewer.vue
<template>
<div ref="container" :style="{ width: width, height: height }"></div>
</template>
<script>
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls';
export default {
name: 'TripoModelViewer',
props: {
modelUrl: String,
width: { type: String, default: '100%' },
height: { type: String, default: '500px' }
},
mounted() {
this.initThree();
this.loadModel();
},
methods: {
initThree() {
// Similar Three.js setup as React example
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
// ... rest of initialization
},
loadModel() {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(this.modelUrl, (gltf) => {
this.scene.add(gltf.scene);
});
}
},
beforeDestroy() {
// Cleanup Three.js resources
if (this.renderer) {
this.renderer.dispose();
}
}
};
</script>
Performance Benchmarking
Track and optimize your AI generated 3D models web performance:
class PerformanceBenchmark {
constructor() {
this.metrics = {
loadTime: 0,
frameRate: [],
memoryUsage: [],
drawCalls: 0
};
}
startLoadTimer() {
this.loadStart = performance.now();
}
endLoadTimer() {
this.metrics.loadTime = performance.now() - this.loadStart;
console.log(`Model loaded in ${this.metrics.loadTime.toFixed(2)}ms`);
}
measureFrame(renderer) {
// Frame ratethis.metrics.frameRate.push(renderer.info.render.frame);
// Memory usageif (performance.memory) {
this.metrics.memoryUsage.push({
used: performance.memory.usedJSHeapSize / 1048576,
total: performance.memory.totalJSHeapSize / 1048576
});
}
// Draw callsthis.metrics.drawCalls = renderer.info.render.calls;
}
getReport() {
const avgFrameRate = this.metrics.frameRate.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / this.metrics.frameRate.length;
const avgMemory = this.metrics.memoryUsage.reduce((a, b) => a + b.used, 0) / this.metrics.memoryUsage.length;
return {
loadTime: `${this.metrics.loadTime.toFixed(2)}ms`,
avgFrameRate: avgFrameRate.toFixed(2),
avgMemoryMB: avgMemory.toFixed(2),
drawCalls: this.metrics.drawCalls
};
}
}
Conclusion: The Future of 3D Web Development
We've covered two powerful approaches to import AI generated 3D assets into web frameworks. The AI-assisted shortcut with Cursor AI democratizes 3D web development, making it accessible to creators without deep coding knowledge. Meanwhile, the traditional manual approach provides the fine-grained control that professional developers need for complex applications.
The combination of Tripo AI's instant AI 3D model generator capabilities and modern web frameworks creates unprecedented opportunities:
-
Rapid Prototyping: From idea to interactive 3D in minutes, not weeks
-
Cost Efficiency: No need for expensive 3D artists for every project
-
Scalability: Generate and deploy thousands of unique models
-
Accessibility: Anyone can create professional 3D web experiences
Whether you're building an e-commerce site with 3D product views, a web-based game, or an educational platform, the workflow from Tripo AI to web deployment has never been smoother. With Algorithm 2.5 generating stunning models in just 8-10 seconds, and the import methods we've covered, you're equipped to create experiences that would have been impossible just a few years ago.
Ready to transform your web projects with AI-powered 3D content? Join over 2 million creators already using Tripo AI. Generate your first model free and see it come to life in your browser within minutes. The future of web 3D isn't about complex workflows—it's about bringing ideas to life instantly.
Start creating today, and discover why Tripo AI is the preferred choice for developers and designers worldwide. Your next breakthrough 3D web experience is just a few clicks away!
Advancing 3D generation to new heights
moving at the speed of creativity, achieving the depths of imagination.

