
3D Model Ancient Human Form: Virtual History
The world of anthropology is changing fast with 3D modeling. It lets us see ancient human forms, like Neandertals, in new ways. These digital models help scientists and also connect people to our shared past.
By making detailed 3D models, researchers can learn more about our ancestors. They can see how our ancestors lived and what made Neandertals different. For example, the Kebara 2 skeleton is about 60,000 years old. It's a key piece for studying how humans evolved.
This is just the start of a journey into virtual history and anthropology. We'll explore new projects and discoveries that are changing how we see our past.

Key Takeaways
- 3D modeling techniques facilitate a deeper understanding of ancient human forms.
- The Kebara 2 skeleton offers significant insights into Neandertal anatomy.
- Virtual history engages the public in cultural heritage and anthropology.
- Neandertals existed for around 360,000 years, leaving a profound impact on our understanding of human evolution.
- Advancements in digital reconstruction enable new discoveries in archaeology.
Introduction to 3D Modeling in Anthropology
3D modeling has changed anthropology a lot. It helps researchers make detailed digital models of ancient humans. This lets them study and see fragile fossils in a new way.
In the Late and Terminal Classic periods of the Maya, from AD 250 to 950, researchers study subadults. They look at how culture and environment affected their growth. The fragile remains from caves in central Belize need special care.
Click to Watch Video Tutorial.
The Maya Bioarchaeology Lab uses photogrammetry for 3D modeling. This tech makes digital models of bones, helping measure them in 3D. It shows how different groups of people were by looking at their bones.
Only 5% of bones are found during digs. 3D modeling helps fill in the gaps. It lets researchers collect and analyze data even without all the bones.
The CRANE project has been working for over a decade. It shows how 3D scanning helps keep studies going long after they're done. It also brings together researchers from all over to study human evolution.
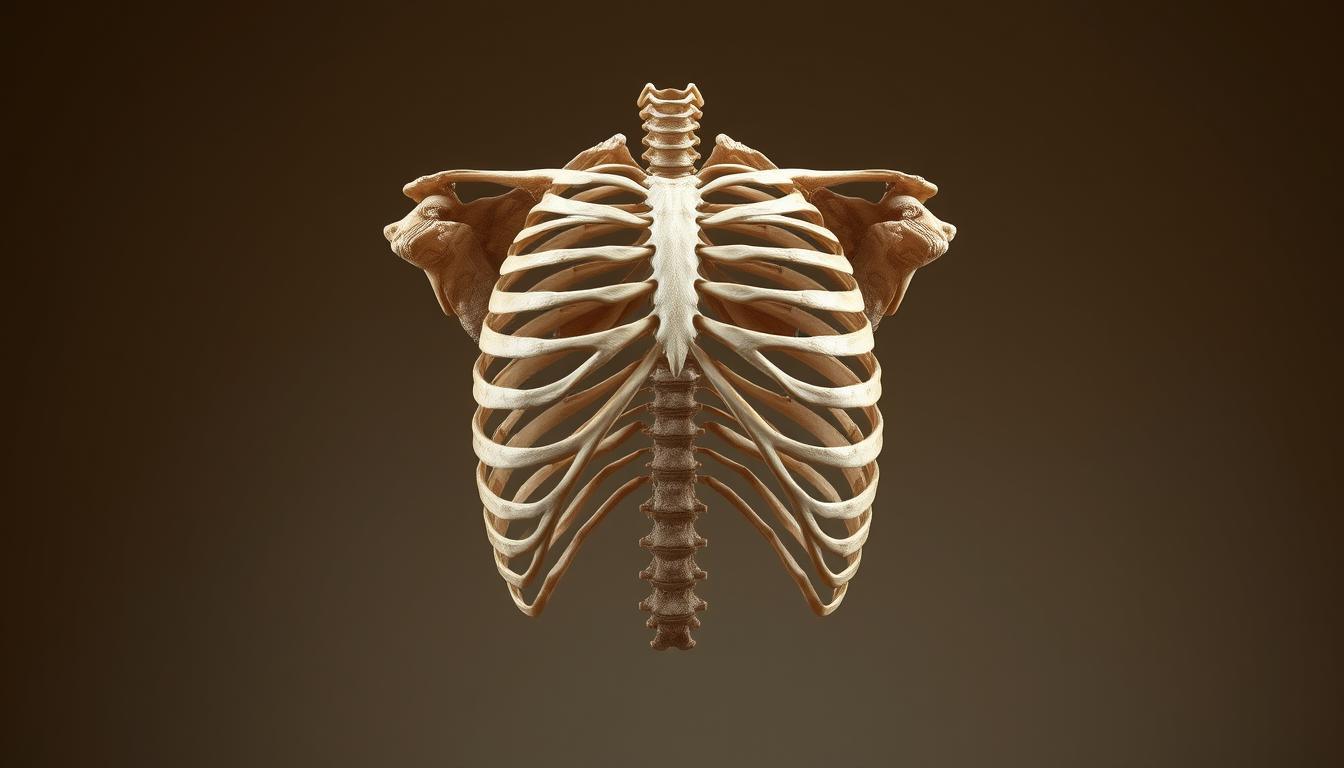
Exploring the Ribcage of Neandertal - A New Perspective
The Kebara 2 Neandertal skeleton is about 60,000 years old. It gives us a peek into the bodies of our ancient relatives. Scientists used virtual reconstruction and CT scans to study its thorax. They found that Neandertals were not hunched as we thought.
The lower part of their ribcage is wider. This means they had bigger lungs and a larger diaphragm. This is different from us and shows they could stand up straight better than we thought.
The Kebara skeleton is the most complete adult Neandertal thorax found. Its ribs are shaped like a B when seen from above. This shows how their chest was different from ours.
This study changes how we see Neandertals. It shows they could live in many places. It also tells us about the evolution of humans and Neandertals.
3D Model Ancient Human Form: Understanding Evolution
3D modeling has greatly helped us learn about ancient human evolution. It shows how Neandertals and modern humans differ. By studying Neandertal features, we gain insights into their lifestyle and adaptability.
This study also shows our connection to Neandertals. It helps us understand our own evolution better.
Significance of Neandertal Features
The Kebara 2 Neandertal skeleton is about 60,000 years old. It was studied with CT scans to make a 3D model of its thorax. This model showed a key difference: Neandertals had a wider lower thorax than modern humans.
This shape suggests they had bigger lungs. They might have used their diaphragm more for breathing. Modern humans use both diaphragm and rib cage for breathing.
Differences Between Neandertals and Modern Humans
There are many differences between Neandertals and modern humans. For example, Neandertals had a spine that was more stable in their thorax. This shows they had special adaptations for survival.
Virtual reconstruction has given us new views on Neandertal biomechanics. It helps us see their importance in human evolution.

The Role of Virtual Reconstruction in Archaeology
Virtual reconstruction changes how we study ancient things. It lets us look at delicate artifacts and fossils safely. This way, we can learn about old cultures and places without damaging them.
It's very helpful for studying fossils that are too fragile to touch. By making detailed models, we can understand history better. This helps us see what life was like long ago.
Benefits of 3D Modeling for Fragile Fossils
3D modeling is great for studying fossils that are easily broken. It lets us study them without hurting them. This is very important.
- Non-invasive exploration: We can look at fossils closely without damaging them.
- Enhanced accessibility: People can see these models online, making history more interesting.
- Rich educational resources: These models are great for teaching, making learning fun.
Case Studies in Virtual Reconstruction
Many examples show how 3D modeling helps in archaeology. For example, the British Museum has shared 3D models online. These have been seen by hundreds of thousands of people.
The models of the Happisburgh Footprints, from 800,000 years ago, have given us new insights. Other examples include:
| Artifact | Year | Technique | Photographs Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Akkadian Brickstamp | Ancient | 3D Modeling | 88 |
| Jericho Skull | Ancient | Photoscan | 138 |
| Pompeii Gladiator Helmet | Ancient | 3D Modeling | 140 |
These examples show how 3D modeling helps us understand history. It also makes history more interesting for everyone. As technology gets better, we'll find even more about the past.
The Uffizi Project and Cultural Heritage
The Uffizi Project is a big effort to make ancient sculptures digital. It focuses on the Uffizi Gallery, Pitti Palace, and Boboli Gardens. Started in 2016, it aims to share art with more people, helping them connect with history.
Digitizing Ancient Sculptures for Accessibility
This project has digitized over 300 art pieces. It uses 3D modeling to let people see these works online. This makes art history more accessible, reaching out to scholars, teachers, and art lovers everywhere.
Benefits of Engaging with 3D Models Remotely
Exploring 3D models online opens up endless possibilities. It helps many people and boosts learning in art and history. Indiana University, Politecnico di Milano, and the University of Florence work together on this project. They make sure the digital models are of high quality and free for everyone.
Advancements in Photogrammetry
Recent tech has changed 3D modeling, moving from laser scanning to photogrammetry. Digital cameras are now used, making data gathering cheaper and faster. The global photogrammetry market is expected to hit $1.9 billion by 2025. This shows how important it is for saving history.
Transition from Laser Scanning to Digital Cameras
Photogrammetry is now a key tool, thanks to digital cameras. It needs about 60-80% overlap in images for accurate 3D models. This method is faster and cheaper than laser scanning, which is great for saving time and money.
While laser scanning is still used for detailed work, photogrammetry is quicker. It can get the needed data in hours, not days or weeks. This is a big plus for archaeological projects.
Impact of Technology on Historical Preservation
Technology has a big impact on saving history. Photogrammetry creates lots of data, like high-res images and detailed models. But, it needs strong computers to process and store this data.
It can also face issues like bad lighting or low-quality cameras. But, it's still very useful for quickly documenting and rebuilding artifacts. This is crucial for protecting cultural treasures that might get damaged or lost.
Looking into new tech in this area helps improve how we document and study artifacts. It also helps us save them for the future. For more on using digital preservation in archaeology, check out this research.

Project Cicero - Virtual Time Travel Exploration
Project Cicero is a big step in virtual time travel. It lets us explore ancient cities like Rome. It uses new tech to make Rome look like it did in its best times.
Users can walk through streets with old buildings. This shows off the city's old architecture. It's a chance to learn and discover.
The goal is to understand ancient cultures better. By exploring Rome's past, we get a clear view of life back then. It's not just about buildings; it's about how people lived and interacted.
This new way of learning history is exciting. It makes history come alive. It turns learning into an adventure.
More people are interested in virtual worlds. Soon, millions will explore these simulations. It's a mix of tech and curiosity that shows how we might see history differently.
This mix of imagination and research could give us new insights. It could help us understand ancient cities better. We might learn more about how they changed and how people lived.
Future of Virtual Reality in Archaeology
Virtual reality is changing archaeology in big ways. It combines new technology with studying old civilizations. This lets us learn in new, exciting ways.
Projects like "Pompeii VR" show how 3D models can bring history to life. Places like the British Museum use it for virtual tours. Over 1,200 people have joined in, showing how much they love it.
Virtual reality makes learning easier for everyone. It helps students who can't afford trips to museums. As technology gets better, learning will become even more personal.
But, there are challenges like getting sick from VR. About 45% of users feel bad. Working together, tech experts and archaeologists can make it better.
The future looks bright for VR in archaeology. We might see virtual digs and more people helping out. It could change how we learn about history, making it fun and accessible for everyone.
Conclusion
3D models have changed how we study ancient human history. They help us understand our cultural heritage better. This technology lets us see how early humans lived in a new way.
At the Olorgesailie Drilling Project, we found 1.5 million years of human history. The Laetoli Footprint Trails give us amazing views of our past. 3D models make exploring our history richer.
Virtual reconstruction has improved how we study ancient humans. It lets us see their anatomy in new detail. For example, we can see how Neandertals were different from us.
As 3D models become more common, they promise to change our studies. They make our research more precise and interesting. This is good news for scholars.
Technology will play a bigger role in archaeology soon. We need to use these tools to keep our history alive. 3D modeling helps us share our human story with others.
By using digital tools, we can make our cultural heritage more accessible. This is a great chance to change how we see our history. It's exciting to think about what the future holds.
FAQ
What is 3D modeling in anthropology?
3D modeling in anthropology uses digital techniques. It creates virtual models of ancient humans. This helps researchers study their anatomy and history without harming fossils.
How does 3D modeling enhance our understanding of Neandertals?
3D modeling shows big differences in Neandertal anatomy. It reveals their ribcage structure. This gives new insights into their biomechanics, posture, and adaptability.
What are some key benefits of virtual reconstruction in archaeology?
Virtual reconstruction lets us explore fossils without harming them. It creates immersive learning experiences. It also makes history and culture more accessible to everyone.
How has the Uffizi Project made art more accessible?
The Uffizi Project uses 3D modeling to digitize ancient sculptures. This lets art lovers and scholars see these masterpieces online. It makes art history available worldwide.
What technological advancements have impacted 3D modeling?
New photogrammetry and digital cameras have changed 3D modeling. They make it faster and cheaper. This helps preserve history more efficiently.
What is Project Cicero and its importance?
Project Cicero recreates ancient Rome's urban landscape with virtual technology. It offers immersive learning experiences. This helps us understand history and cultural progress better.
What future trends can we expect in virtual reality for archaeology?
VR technology will get even better. We'll see more interactive experiences with historical artifacts. This could change how we learn about and interact with archaeological finds.